Utilize on-street parking as a vital resource in expanding capacity of development and districts in high-demand.
Maintain parallel parking on-street wherever possible to provide greater accessibility to a number of modes, such as bicyclists and pedestrians. Consider angled on-street parking on streets with lesser traffic volumes while not inhibiting other modes to serve as a traffic calming tool. The angle of on-street parking will influence the character of the street.
Provide back-in angled parking in conjunction with bicycle lanes or provide a separated bikeway between the parking and the sidewalk. Avoid head-in angled parking because drivers entering and existing may not see bicyclists.
Maximize and better manage curb space by clearly marking on-street parking spaces via “L” or “T” shaped space boundaries.
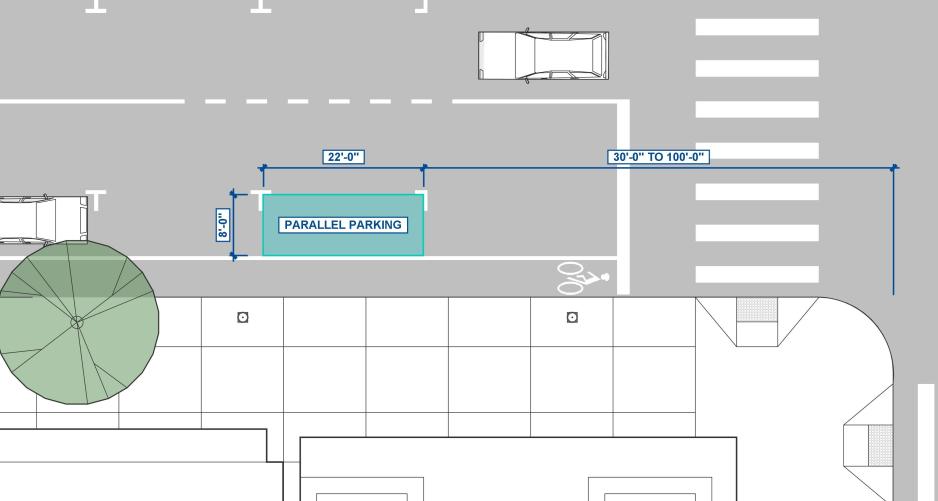
Consider standard dimensions for on-street parallel parking at eight (8) feet wide by 22 feet long and 30 to 100 feet from any intersection depending on the design speed.
Employ tools to utilize on-street parking as short-term parking with pricing or time limits.